|
The Variety of Life
What you should know.
- Living things feed, grow,
move, reproduce, respire, get rid of waste and use senses.
- Living things need energy
from food.
- Energy is released from
food during respiration.
- Plants use sunlight to
make food by photosynthesis.
- Living things can be put
into groups that have similar features.
- Plants and animals of one
kind are called a species.
- Animals with backbones
are called vertebrates, those without are called invertebrates.
- Some plants make seeds to
reproduce, others make spores.
- Water is carried around
plants in tubes called xylem.
- Cells are made up of a
membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus.
- Plants use chloroplasts
to trap light energy for photosynthesis.
- Some cells have changed
their shape to do special jobs.
- The main parts of the
human body.
- The main parts of a
flowering plant.
Every part of the world is teeming with life - from the
air to the land, the sea to the rivers, the volcanos to the poles! The variety
of life on our planet is wide and exciting! We are going to learn all about some
of the life on earth during this section.
The 7 life processes are what all living organisms do.
You must learn these for the exam. A good way of doing this is remembering the
phrase "Mrs Gren"
| M |
Movement |
Animals move to
find food and away from predators. Plants move towards light.
|
| R |
Reproduction |
Both animals and
plants reproduce to make their species carry on.
|
| S |
Sensitivity |
Animals and
plants are sensitive to light.
|
| - |
|
|
| G |
Growth |
Animals grow
larger and stronger which helps them hunt better.
|
| R |
Respiration |
Animals and
plants must turn their food into energy.
|
| E |
Excretion |
Waste products
must be excreted from plants and animals.
|
| N |
Nutrition |
Animals need
food for respiration and plants need minerals from the soil.
|
All living things can be split into groups. These
groups can be further split because of features shared by some living creatures.
i.e. we can split living things up into plants and animals. Plants make their
own food by trapping the suns energy in a chemical reaction called
photosynthesis. Animals get their food by eating plants or other animals.
Animal Groups
Animals can be split into 2 main
groups
- invertebrates - no backbone
- vertebrates - have a backbone
We looked further at these groups and in particular at
vertebrates splitting them into 5 main categories:- mammals, birds, fish,
reptiles and amphibians - and looked at their group characteristics that we use
to put them into these groups.
| Mammals

|
- give birth to live young
- have hair or fur
- suckle their young
- are warm blooded
|
| Fish
|
- breathe with gills
- have scales
- lay eggs
- live in water all the time
|
| Birds

|
- have feathers
- have wings
- lay eggs with hard shell
- warm blooded
|
| Reptiles
|
- have dry, scaly skin
- lay eggs with soft shells
- have lungs
- are cold blooded
|
| Amphibians

|
- have smooth, moist skin
- breed in water
|
We also look at plants and break them into groups:-
flowering, conifers, ferns and moss. One of the practicals we do is to germinate
beans and yet another is to cut up a bean and see what is inside!
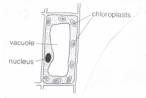
We also learn that all living things are made up from tiny 'building blocks'
we call cells. All cells have a nucleus to control it, a cell membrane that
surrounds it, and cytoplasm which is like a jelly where the chemical reactions
happen. Plant cells also have a cell wall, to make the cell rigid, a large
vacuole and green chloroplasts where photosynthesis happens.
 |
 |
| animal cell |
plant cell |
|
|
Adaptation
|
Job
|
|
Red
blood cell

|
Large
surface area
Shape
allows flexibility
|
To
absorb and carry oxygen around the body
|
|
Sperm
cell

|
Long
tail
|
Able
to swim freely towards egg
|
|
Nerve
cell
|
Long
and wide reaching
|
To
obtain information from a large area and to take allow information to be
sent a long distance
|
|
Plant
cell
|
Rigid
cell wall
Packed
with chlorophyll
|
Support
To
absorb as much sunlight as possible
|
|
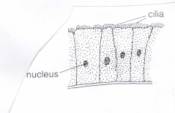
Ciliated
cell

|
Small
hair like projections which can move
|
Allow
transfer of substances
(eg mucus)
|
|
Root
hair cell

|
Large
surface area
|
To
absorb as much water as possible
|
What you should be able to do.
- Plan an investigation to
find out if seeds are living or not.
- Make a table of
differences between plants and animals.
- Name the main groups of
invertebrates, vertebrates and plants.
- List the main features of
each group of invertebrates, vertebrates and plants.
- Put an animal or plant
into the correct group.
- Cut open a seed and find
the different parts.
- Plan an investigation to
find out which leaves lose most water.
- Use the following words
correctly: Cell, Tissue, Organ, System.
- Work out the actual size
of a cell.
- Make a slide of some
onion skin.
- Use a microscope to look
at cells.
- On a diagram, label the
parts of the microscope.
- Cut and stick together
the main organs of the human body.
- Plan an investigation to
get the most dye out of a piece of beetroot.
|