|
Using Forces
What you should know.
- Forces are pushes and
pulls.
- Forces are measured in
newtons (N).
- Forces are measured using
a force-meter, also called newton-meters or spring balances.
- An object can have more
than one force acting on it. If the forces are nor balanced there is a
resultant force. It is the resultant force that moves the object.
- If 2 forces acting on an
object are equal and opposite we say they are balanced forces. In this case
there is no resultant force.
- Weight is a force. It is
the pull of the Earth's gravity.
- When two object rub
together a force called friction slows them down.
- When an object is put in
water the water pushes up, this force is called 'upthrust'.
- Newton's Law: If the
forces on an object are balanced then if it still, it stays still, if it is
moving it continues at a steady speed in a straight line.
- Structures are usually
stronger if they are built of triangular shapes.
- When a bridge bends some
parts are under compression and others are under tension.
- The bigger the weight on
a simple beam bridge the more it will bend.
- The larger the force on a
spring the more it stretches. Equal weights on a spring make it stretch by
equal amounts, until the spring deforms.
- Average speed = distance
traveled/time taken
- Speed is measured in
metres per second or kilometres per hour.
- If an object speeds up it
is accelerating. If it slows down it is decelerating.
When there is more than one force on
an object:
- If all
the forces are in balance, the object will stay as it is - stationary
or moving - at a steady speed in a straight line.
- If the
forces are unbalanced, it will:
- start
to move in the direction of the force
- speed
up (accelerate)
- slow
down (decelerate)
- change
direction.
Here
are 4 types of forces:
-
air
resistance - drag: when
an object moves through the air, the force of air resistance acts in the
opposite direction to the motion. Air resistance depends on the shape of the
object and its speed.
-
contact
force: happens
when two objects are pushed together. They exert equal and opposite forces
on each other. The contact force from the ground pushes up on your feet as
you push down to walk forwards.
-
friction:
the force
which resists movement between two surfaces which are in contact.
-
gravity:
the force
which pulls objects towards the Earth. We call the pull of gravity on an
object its weight. The Earth pulls with a force of about 10 newtons on every
kilogram of mass.
Remember
Forces
are often represented by arrows (=). The bigger the arrow the bigger the force.
Forces are measured in newtons (N).
Compression
& Tension
We
also look in this module at construction and the difference in strength of
different shapes -particularly for building bridges. A triangular shape is the
best! When a bridge is being squashed from both sides we say it is in compression
and when it is being pulled from both ends we say it is in tension.
Look at this picture of a car and
the forces acting upon it. Then read this typical exam question about mass and
gravity.
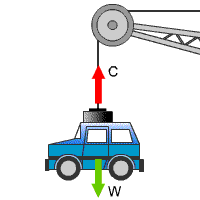
The picture shows a car in a
scrapyard. The mass of the car is 750 kg.
Question 1
What
is the weight of the car?
The Solution
You
should have worked out the weight of the car this way:
|
weight (N) = mass (kg) x
gravitational field strength (N/kg)
|
OR
|
W = mg
|
|
weight (N) = 750 kg x 10 N/kg
|
OR
|
W = 750 kg x 10 N/kg
|
|
weight = 7,500 N
|
OR
|
W = 7,500 N
|
Question 2
What
force does the arrow W represent?
The Answer
The
arrow W is to show the direction of the weight on the car.
Question 3
What
force does the arrow C represent?
The Answer
The
arrow C represents the direction of the force from the crane to
lift the car.
Question 4
What
is the minimum force needed to lift the car?
The Answer
The
minimum force is 7500 N, to overcome the pull of gravity.
Question 5
Suggest
why the force from the crane engine will need to be bigger than your answer to
(d).
The Answer
There
will be some friction in the cables and pulleys, so the force will have to be
bigger.
Do not forget that:
- Weight
is the force of an object due to the pull of gravity.
- Weight
is measured in newtons.
- When
you draw an arrow for a force, label the arrow to show what force it is.
- Gravity
is the force of attraction between any two masses. We only notice the force
if one of the objects is very big - like the Earth, Moon or Sun.
- On the
Earth gravity pulls with a force of 10 newtons for every kilogram (10 N/kg).
We call this the gravitational field strength.
- The
pull of gravity on the Moon is less, because the mass of the Moon is less.
The gravitational field strength of the moon is 1.6 N/kg.
- Gravity
keeps the planets in orbit around the Sun and the moon and artificial
satellites in orbit around the Earth.
- W = mg
means Weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg)
Floating and Sinking
When placed in water some objects float and others
sink. Have you ever wondered why? It is to do with the DENSITY of the object.
This is mass/volume. If an object is more dense than water it will sink and if
it is less dense than water it will float!
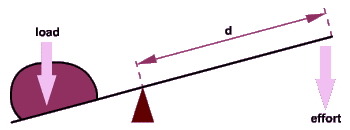
Levers
These
are simple machines because they can make work easier by multiplying
the force you are using.
Forces
can be made to move things by turning the object around a pivot or
fulcrum. It is just like a seesaw; with a downward force pushing on one side, an
object on the other side will move. The downward force of the effort
causes the load, on the other side, to move. When the two forces are
equal there is no movement and the seesaw is balanced or in equilibrium.
Friction
An
object travelling
at speed has a force called friction acting on it to
slow its
motion. It is important to remember that friction isn't all bad.
Friction
between the tyres and the road enables a vehicle to move because the tyres grip
the road. The brakes on a car or bicycle work because of the friction between
the brake pad and wheel rim. We can walk because of the grip between the soles
of our shoes and the pavement.
In
air or water friction is called drag or
air/water resistance.
Energy is needed to overcome these frictional forces and reduces the
maximum
speed we can reach. To reduce friction, the shape of the object can
be streamlined by using curved surfaces and rounded corners.
An
aircraft or object flying in a straight line at constant speed does so because
all the forces are equal. The lift of the wings is equal to the
weight
or downward force caused by gravity. The thrust force of the engine is
equal to the air resistance or
drag caused by the body shape.

Summary
When there is more than one force on
an object:
- If all
the forces are in balance, the object will stay as it is - stationary
or
moving - at a steady speed in a straight line.
- If the
forces are unbalanced, it will:
- change
speed
- change
shape
- change
direction.
What you should be able to do.
- Read the scale on a
force-meter.
- Design and build a
structure from straws to be as strong and as tall as possible.
- Plan an investigation to
find out which shape gives the strongest bridge.
- Design and build a bridge
from paper and straws.
- Plan an investigation to
find out what affects the sagging of a beam bridge.
- Plan an investigation to
see hoe the length of a spring depends on the weight hanging on it.
- Calculate the speed of an
object.
|