|
The Active Body
What you should know.
- The skeleton supports the
body and allows movement.
- The names of some of the
bones in a human skeleton.
- A joint allows movement
of bones.
- Muscles provide the force
needed to move bones.
- Muscles can only pull.
- When one muscle in a pair
contracts the other relaxes. They are 'antagonistic'.
- Many bones work like
levers.
- Cartilage and synovial
fluid reduce friction at a joint.
- Tendons join muscles to
bones. Ligaments join bones to other bones.
- Sports injuries often
affect muscles and bones.
- A reflex is an automatic
that is often protective.
- Sense organs detect
changes around us.
- Muscles are controlled by
messages that travel along nerves.
- Some sports need fast
reaction times.
- Skin is sensitive to
heat, cold, touch, pain and pressure.
- Skin sweats and looks
flushed when it is hot and pale when it is cold.
- How blind people can read
using Braille.
- How some clothes are
designed to cut down heat loss.
- Kidneys control the
amount of water in the body.
- Kidneys remove waste from
the blood and produce urine.
- How a dialysis machine is
used to treat patients with kidney problems.
In this topic we learn all about bones and joints, how to keep healthy,
kidneys and the skeleton.
The skin is a barrier to the outside world against bacteria etc. The skin is
also very sensitive to we can feel things The skin's main function is
temperature control. Below is how the skin is able to change the bodies
temperature
Cooling the body:
Blood capillaries widen (vasodilatation) to bring more blood near the surface of
the skin so heat can be lost into the surroundings by radiation and convection.
Sweat is produced which, as it evaporates, has a cooling effect on the body.
Hairs lie flat which allows warm air to escape faster
Warming the body:
Blood capillaries in the skin become more narrow (vasoconstriction) so less heat
is lost into the surroundings. Sweating decreases so less heat is lost. Hairs on
body stand up on end to trap air which reduces warm air escaping so rapidly
Skeletons and Muscles
The skeleton of any animal has many functions including:
Protection:
The skull protects the brain and the rib cage protects the heart and lungs. The
backbone is important to protect the spinal chord.
Support:
Bones give us shape and a framework for vital organs to be stored safely inside.
Blood formation:
In some bones there is red bone marrow which produces red blood cells.
Movement:
Muscles are attached to bones and bones have joints which allow the body to
move. Animals need to move towards food and away from predators.
Skeleton muscles:
These muscles are attached to the skeleton. A muscle is attached to bones via a
tendon. Muscles that work in pairs are known as antagonistic muscles. When
muscles contract, they pull the bone to which they are attached closer. As one
muscle contracts, the other relaxes. Muscles are effects which respond to
nervous impulses.
Peristalsis is the
movement of muscles to force food along the gut. This happens without our
control.
There are two main types of joints (where two bones
meet):
Hinge joints: Move in one direction like a hinge. Up and down. e.g. knee
joint
Ball and socket joints: These can move in many directions freely. e.g.
shoulder
You can feed any desire to see inside real
animals and learn about the function of the internal organs. Safe in the
knowledge that no scalpels or frogs will be used in the lesson, they can dissect
a frog at http://homeworkhelp.about.com/teens/homeworkhelp/gi/dynamic/offsite.htm?site=http://www%2Ditg.lbl.gov/vfrog/dissect.html.
The 'Inner body' at http://www.innerbody.com/htm/body.html
allows you to find out the size, weight, location and function of each human
body organ.
Some sites that may help you are:-
These are super skeleton sites that name bones and show
you all about them and joints.
http://www.gwc.maricopa.edu/class/bio201/muscle/mustut.htm
This site tells you all about muscles
|
|
Adaptation
|
Job
|
|
Red
blood cell

|
Large
surface area
Shape
allows flexibility
|
To
absorb and carry oxygen around the body
|
|
Sperm
cell

|
Long
tail
|
Able
to swim freely towards egg
|
|
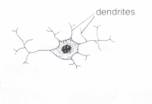
Nerve
cell
|
Long
and wide reaching
|
To
obtain information from a large area and to take allow information to be
sent a long distance
|
|
Pallisade
cell
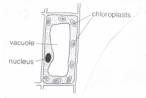
|
Rigid
cell wall
Packed
with chlorophyll
|
Support
To
absorb as much sunlight as possible
|
|
Ciliated
cell
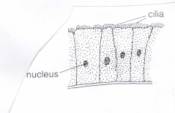
|
Small
hair like projections which can move
|
Allow
transfer of substances(eg mucus)
|
|
Root
hair cell

|
Large
surface area
|
To
absorb as much water as possible
|
What you should be able to
do.
- Match the joints to their
type of movement.
- Investigate how the
length of a straw changes its strength.
- Find out which muscle
contracts and which relaxes when the arm and leg move.
- Test your finger strength
in an investigation.
- Make a model arm to show
how the muscles work.
- Locate three levers found
in the human skeleton.
- Carry out 4 trials of
strength and find out which muscles are used.
- Investigate 4 reflexes
and know why they are useful.
- Measure your reaction
time with a falling ruler.
- Describe how the reacts
to different water temperatures.
- Carry out an experiment
to find out which parts of the hand and arm are the most sensitive to touch.
- Carry out an experiment
to show that a small animal cools down more quickly than large animals.
- Interpret data on the
effect of temperature on the amount of sweat and urine produced.
- Explain the differences
in the amounts of chemicals in the blood and in the urine.
|