|
Acids & Alkalis
What you should know.
- Acids and alkalis are
chemical opposites.
- Indicators are used to
show which substances are acids and which are alkalis.
- Litmus turns red in acid
and blue in alkali.
- Universal indicator shows
how strong or how weak acids and alkalis are.
- Acids have pH numbers of
less than 7.
- Alkalis have pH numbers
of more than 7.
- Acid rain is made when
burning makes acidic gases.
- Acid rain damages
buildings and trees.
- Neutral solutions can be
made by mixing acids and alkalis.
- Neutral solutions have a
pH number of 7.
- The pH of soil can
changed to suit different plants.
In this topic we learn that all liquids can be either
an acid, an alkali or neither (neutral). We learn to be able to distinguish
between them using an indicator. We also get to make our own indicators.
What is an acid?
When a substance dissolves in water, the
solution may be acidic,
neutral or alkaline.
The three common acids you will find in
the laboratory are
1) Hydrochloric acid - HCl(aq)
2) Nitric acid - HNO3(aq)
3) Sulfuric acid - H2SO4(aq)
They are all strong acids
They have a pH less than 7, see pH. They
will turn blue litmus
paper red. When an acid
reacts with an alkali,
it forms a neutral salt
and water. This is called neutralization.
hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide ▒
sodium chloride + water.
HCl(aq) +
NaOH(aq) ▒
NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
All metal oxides and hydroxides are bases. Those which
dissolve in water are known as alkalis - they neutralise acids to produce a salt
and water.
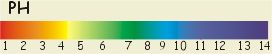
The pH scale measures how acidic or alkaline a solution
is. It goes from 1 to 14. pH1 is a very strong acid, pH14 is a very strong
alkali and pH7 is neutral.
What you should be able to do.
- List five words which
relate to acids.
- Make indicators from
berries, petals or vegetables.
- Plan and do an
investigation to see which indicator is best.
- Draw diagrams of a
mortar, pestle, beaker, test-tube and pipette.
- žUse a colour chart to
work out a pH number.
- Investigate to how acid
rain affects stonework.
- Carry out tests to
neutralise stomach powders.
- Measure the pH values of
different soils.
- Filter a solid/liquid
mixture.
- Use a plant preference
chart to match crops to different soil types.
|